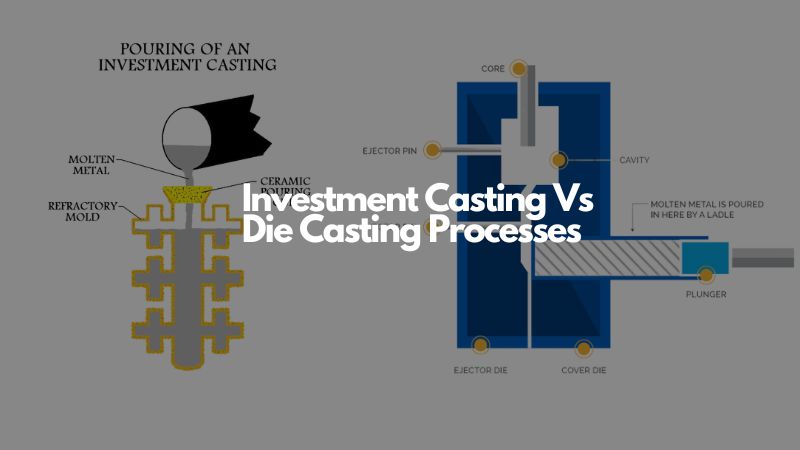
This guide compares all fundamental variables of investment casting vs die casting. It will help you choose cost-effective and efficient casting technology for your foundry shop
Let’s dive right in:
What is Die Casting?
Dies casting involves pouring molten metal in mould to make parts. The final metallic parts takes the shape of the mold.
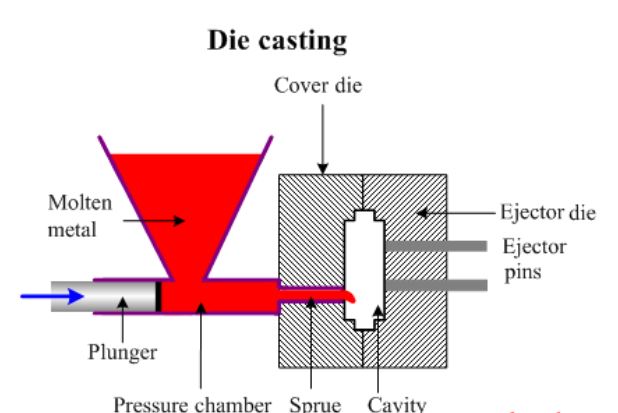
Die Casting
What is Lost Wax Casting?
Unlike die casting, you will use mould made from wax to make pattern. With the mould ready, you will simply pour molten metal.
First, you will make a wax pattern. There after the wax pattern is dipped in ceramic liquid, allowing it to cool. You will then melt the wax to remain with the pattern – mold.
Investment Casting
Die Casting Vs Lost Wax Casting Advantages
| Advantages of Investment Casting | Die Casting Advantages |
|
|
Disadvantages of Investment Casting Vs. Die Casting
Like any other metal casting process, both lost wax casting and die casting have unique limitations. So, even as you choose these materials for specific metal casting process, you should have ways to deal with the challenges.
| Disadvantages of Investment Casting | Disadvantages of Die Casting |
|
|
Die Casting Process Vs Investment Casting Process
Die casting and investment casting are both metal manufacturing procedures that require you to add or pour liquid metal into moulds. I will explain step by step how each method works. From here you can now choose the method that works for your manufacturing needs.
Die Casting Process
Die Casting Process
Step 1: Making Mould or Getting Mould Ready for Casting
For die casting, first, consider getting a hardened steel for making that mould or cavity in the desired shapes. Once your mould or die has been built, you need to prepare it for casting purposes. You can actually use water mixed with a lubricant for cleaning and getting the die ready for operations.
Step 2: Clamping Mould Together
Once your die or mould is cleaned and dry, you need to clamp the halves of the moulds together under pressure. This allows the liquid metal to flow in and reach every part of the mould.
Step 3: Melting Metal and Pouring into Mould
After filling your mould with liquid metal, you need to let it cool down until it can form a solid. The time required for cooling is not standard for all metals, some take longer than others. This is determined by the wall thickness, geometry and type of the metal used.
Step 4: Ejecting Part from the Mould
At this stage, your part has been formed and is ready for ejection. You simply need to separate the two halves of the mould. Use the ejection mechanism designed for the machine to eject your parts. You should be keen and pay attention to the force applied during ejection to avoid damage.
Step 5 Deflashing Mould
After ejection, you can trim your parts through a process called deflashing. Doing this helps you get a clean and smooth part free from excessive material. At this point, your part is ready for the desired usage.
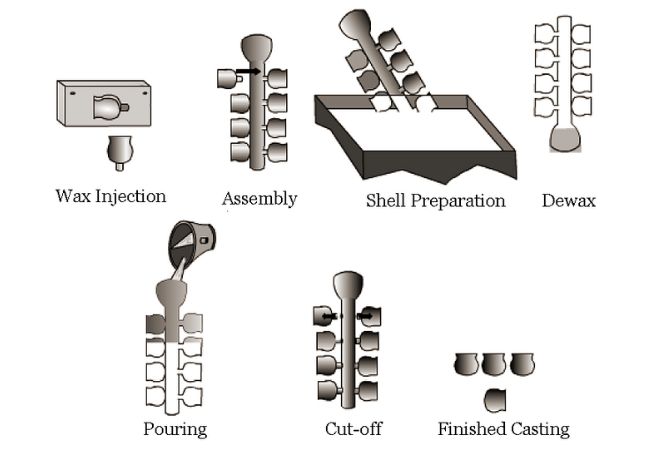
Investment Casting Process
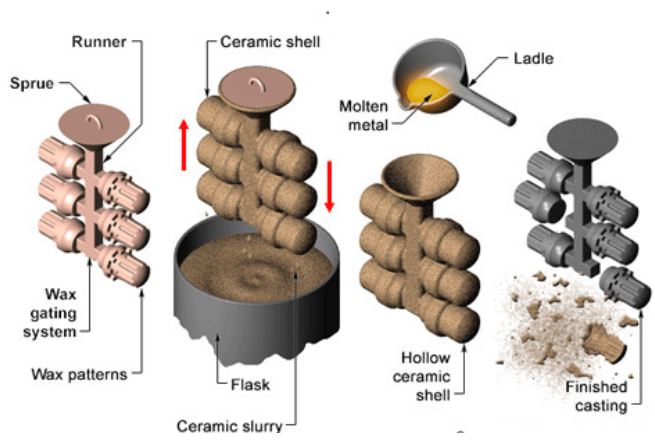
Investment Casting Process
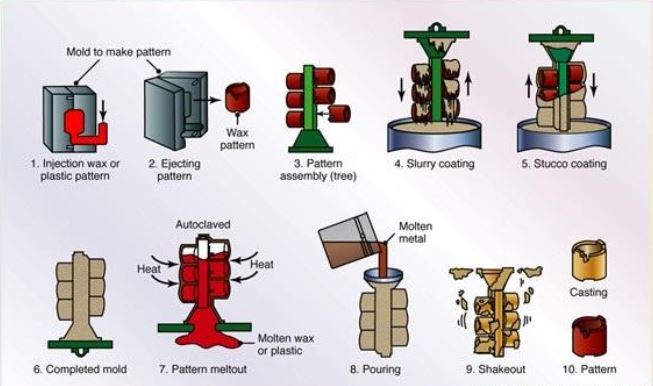
Step 1: Design Pattern
The first step in investment casting is to design and create the desired pattern. Make your pattern while making sure to leave an allowance for possible shrinkage. Use wax for creating patterns within the mould.
Step 2: Make Patterns Using Wax
After getting the right patterns for your parts using wax, you have to combine them. This will help you to come up with a system that has both metal delivery and runner. This will form the kind of tree you desire for your parts.
Step 3: Dip Wax Tree in Ceramic Solution
Dip your tree into a liquid ceramic then cover it using a sand stucco and let it dry. Repeat this process (dipping and drying) until you get the required thickness. Once the shell has been dried fully, it is now ready for the casting process.
Step 4: Remove Wax to Make Final Mould for Casting
Once your assembly or tree is dry and is in the shape of your desired parts, place it in an autoclave. The wax melts away and in case of any residue, burn it out by placing the assembly in a furnace. Also, your ceramic assembly gets stronger and stable passing through the high temperatures.
Step 5: Melt Metal Ready for Casting then Pour in Mould
Here you need to melt the metal and get your mould ready by heating it to the require temperature. Pour your liquid material into the preheated ceramic mould. Remember that you can use either vacuum or air melting procedures to liquify your metal depending on the metal type.
Step 6: Remove the Pattern
Allow the liquid metal a sufficient time to cool before employing the knockdown operation to remove the ceramic shells. Take your parts through secondary procedures like machining, grinding or sandblasting. After finishing, carry out quality tests using magnetic particles, fluorescent penetrant etc.
Before shipping your parts, inspect things like dimensions, alloy tests etc.
Techniques in Investment Casting Vs Die Casting
Let’s look at:
Processes in Die Casting
The major options include:
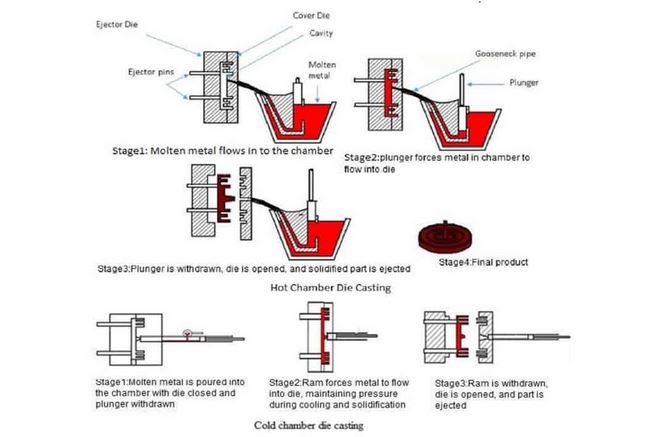
- Hot chamber die casting
- Cold chamber die casting
However, depending on the task at hand, you may consider:
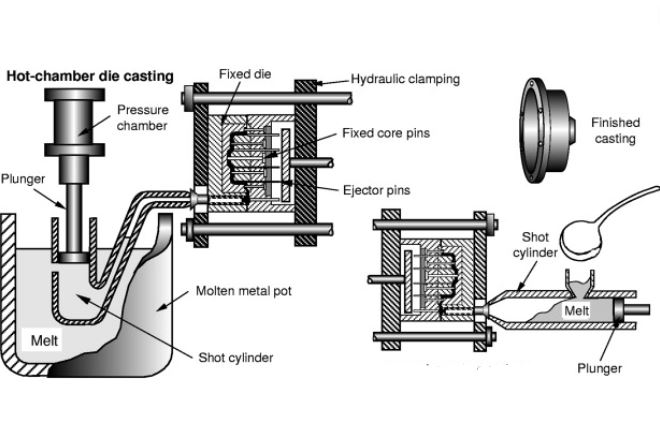
Gooseneck/Hot Process:
In this process, your cylinder chamber has be fully submerged into the liquid metal bath. From here, part of the die in the shape of a gooseneck draws the liquid into the mould cavity.
This process is suitable for:
- Zinc
- Copper
- Magnesium
Generally, these metals have low melting point. At the same time, they are popular for high fluidity.
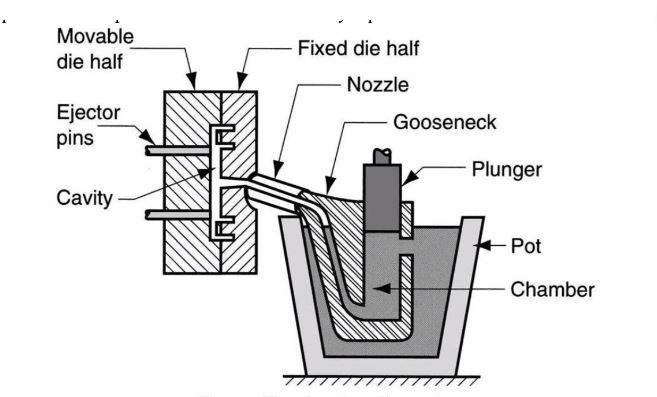
Hot Chamber Die Casting
Cold Chamber Process:
In this method, you don’t have to dip in the injection system of the mould or die into the liquid metal bath. All you to do is deliver the liquid metal into the system through a designed delivery mechanism.
This method is meant to reduce the amount of corrosion caused to the machine. Aluminium and alloys are better die-casted using this process.
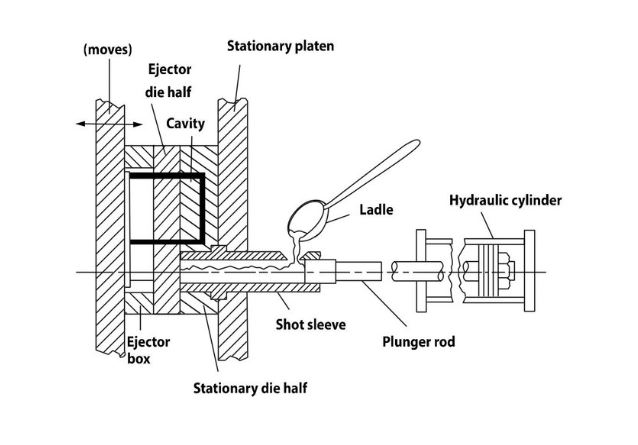
Cold Chamber Process
Low Pressure Process:
There are parts that are circular or round in shape like a wheel. In order to get the shape of this part right during die casting, you need a low pressure injection method. For these parts your die is positioned above your liquid bath. The two are joined using a rise pipe.
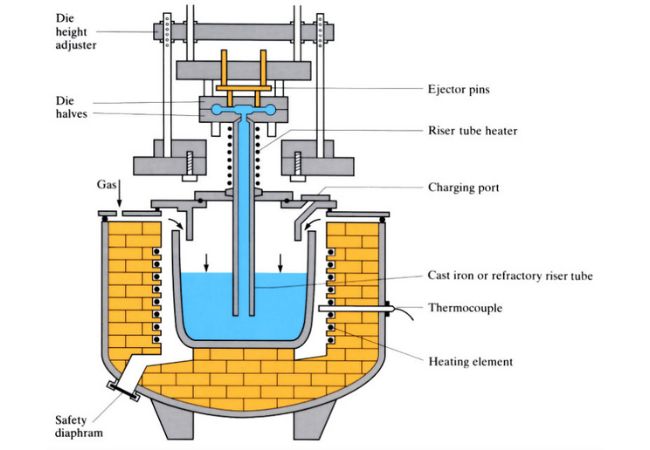
Low Pressure Process
At this point, apply just low pressure to enable the liquid metal to rise and pour into the mould.
Vacuum Process:
Vacuum die casting process uses low pressure similar to what the low-pressure method applies. However, for this method, the liquid metal bath is positioned above the mould. The vacuum created in the chamber enables the liquid metal to pour into the die.
Vacuum Process
Squeeze Process:
For this case, the die is open and once the liquid metal is poured in, it closes. At this point your liquid metal is squeezed and is forced to spread evenly into the die. You can choose this process for metal parts that are dense and must be heat treated.
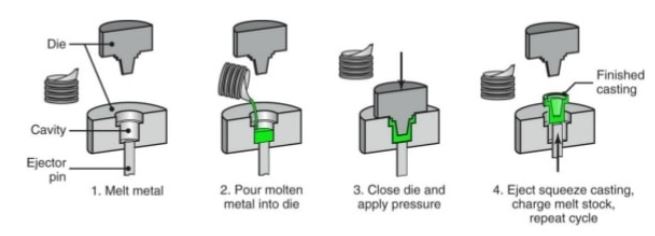
Squeeze Process
Semi-Solid Process/Thixoforming.
This process is useful when you need to minimize porosity and achieve highly dense products. You have to cut you material into pieces, heat to phase transition from solid to liquid to achieve your slushy texture. Inject it into the mould and allow it to cool and solidify.
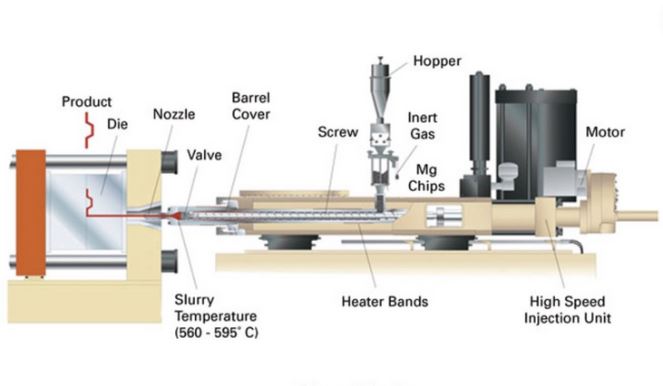
Semi Solid Process
Type of Investment Casting Process
Some popular technique are:
Lost Foam Casting:
The material to be used for this process is designed in the form of beads. All you need to do is to add them into the mould then melt them by raising temperature of the machine.
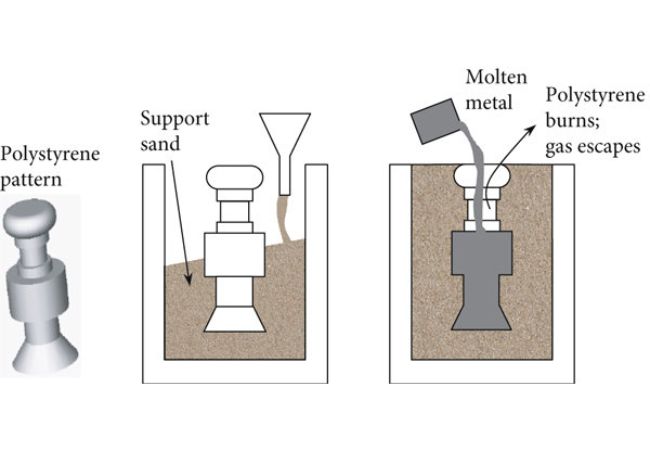
Lost Foam Casting
Once the material has melted, it will fill the cavities of the mould.
Direct Investment Casting:
For this method, you need a prototype made by a machine or hand. You will use the prototypes for the production of the required metal parts.
Direct Investment Casting
Water Glass Investment Casting:
This investment casting process is similar to the other casting processes except that it uses a water for binding purposes.
Water Glass Investment Casting
Investment Casting and Die Casting Materials Selection
In both cases, you can cast parts from non-ferrous metals. These may include:
- Aluminum
- Magnesium
- Zinc
Ferrous metals can be casted using lost wax technique. Recently for complex stainless steel and copper parts, investment casting has proved to be a perfect option.
When to Choose Die Casting or Lost Wax Casting
You actually need to consider several key factors before settling on either die casting or investment casting. The details described below will give you a hint on which casting method to go for.
Choose die casting when;
- You deal in high quantity production process
This is because die casting is a quite expensive investment and may not give any revenue when producing in low quantities.
- You need speed
Due to repetitive nature, casting speed is high.
- You produce larger parts
Unlike lost wax casting, die casting can make extremely large parts. However, you may incur more costs in terms of machinery.
Choose investment casting when;
- Your company deals in both non-ferrous and ferrous metals. Like I mentioned in the above subtopic, investment casting can create parts from these metal types.
- You need design freedom. Investment casting is generally very flexible and parts with net shape or complex designs can be produced with less effort.
Conclusion
Generally, metal casting is a process that has been evolving over the years. Right now, there are several challenges that have been resolved through the new technology and developments.
Both investment casting vs die casting differ in various ways including the metal types, production size, complexity, design freedom.
You need to really consider what your needs are and compare the two processes before you make a choice. Alternatively, you can consult an expert for further directions.
For all your die casting, contact us now.
More Resources:
Investment Casting Tolerances – Source: UCASTING
Die Casting – Source: Wikipedia
Investment Casting Process – Source: UCASTING
In-house Tooling for Investment Casting – Source: UCASTING
Lost Wax Casting – Source: The Crucible



